*Treatment of Catastrophic Bleeding – Wound Packing*
Haemostatic Dressings
If a wound is deep and bloody and bleeding cannot be stopped with direct pressure you need to pack it - ideally with a haemostatic dressing.
These dressings are treated with an agent or chemical that assists with the formation of blood clots and will stop the bleeding more quickly.
If you don't have a haemostsatic dressing, use any bandages, gauze or clean cloth available.
Note: Haemostatic dressings are not suitable for wounds to the chest, airway, eyes or the head if brain tissue is exposed
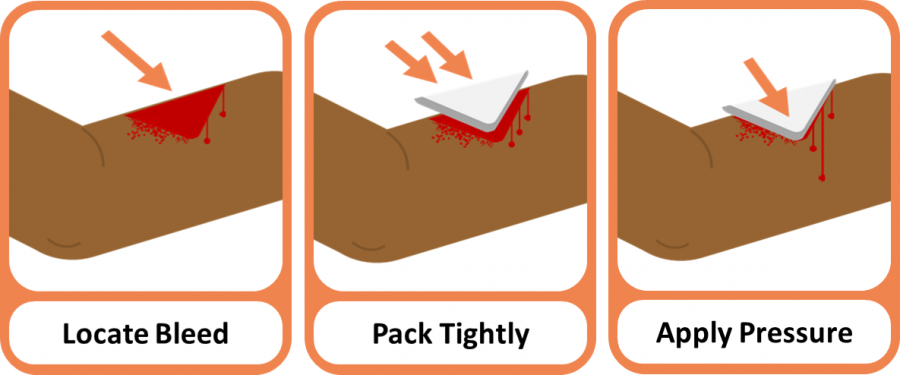
Wound Packing - Step by Step
Suitable for deep wounds to the shoulders, armpit, buttocks and groin
DO NOT pack wounds to the neck, chest or abdomen
- Move any clothing away to expose the wound
- Place your gloved fingers — with or without a dressing — into the wound to apply initial pressure to the exact point of bleeding (the vein, artery or both). You may need to mop away excess blood to locate the source of the bleeding.
- Keeping pressure on the bleed, use your other hand to tightly pack the wound with a haemostatic dressing, bandages or other clean cloth
- Ensure the dressing or cloth reaches as deep into the cavity as possible and stuff to capacity
- Apply very firm direct pressure with both hands directly on top of the bleeding wound for at least 10 minutes (approximately 3 minutes if you are using a haemoststaic dressing)
- If bleeding is under control, secure the wound packing with another dressing
- Maintain pressure until medical help arrives. Inform medical professionals about the materials you have used to pack the wound
